开发笔记
1. 导入百万级别的Excel数据
这里有2个要解决的问题:
- 如何将百万数据从Excel文件写入内存
- 如何将百万数据从内存写入数据库
1.1 Excel读取文件的写法
Tips
先说结论,能用EasyExcel,直接用
- 最原始的,通过APACHE POI读取
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi</artifactId>
<version>4.1.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId>
<version>4.1.2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
public class PoiExample {
public void importExcel(InputStream inputStream){
try{
Workbook workbook = WorkbookFactory.create(inputStream);
for(Sheet sheet:workbook){
for(Row row:sheet){
for(Cell cell:row){
System.out.println(cell.getStringCellValue());
//...
}
}
}
}catch (Exception e){
}
}
}
Note
解析效率低。
处理大文件容易OOM。
- 通过Hutool的ExcelReader
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutool</groupId>
<artifactId>hutool-all</artifactId>
<version>5.8.29</version>
</dependency>
public class HutoolExample {
public void importExcel(InputStream inputStream){
ExcelReader reader = ExcelUtil.getReader(inputStream);
//方式1:读取后,每一行数据封装成Map,默认第一行为标题行,Map中的key为标题,value为对应的单元格值
List<Map<String,Object>> data1 = reader.readAll();
//方式2:读取后,每一行数据封装成Bean,默认第一行为标题行,Bean中的字段名为标题
List<Student> data2 = reader.readAll(Student.class);
}
}
Note
简单地对POI进行封装,方便用户开发
- 通过EasyExcel
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>easyexcel</artifactId>
<version>${easyexcel.version}</version>
</dependency>
示例代码见:https://easyexcel.opensource.alibaba.com/
Note
解决了POI大文件内存容易溢出的问题
- 通过StreamingReader
<dependency>
<groupId>com.monitorjbl</groupId>
<artifactId>xlsx-streamer</artifactId>
<version>2.2.0</version>
</dependency>
public class MonitorJBLExample {
/**
* 导入示例代码
* @param inputStream
*/
public void importExcel(InputStream inputStream){
int rowCacheSize = 200; //缓存到内存中的行数(默认10行)
int bufferSize = 10240; //缓存到内存中的默认大小(默认1024字节)
Workbook book = StreamingReader.builder().rowCacheSize(rowCacheSize).bufferSize(bufferSize).open(inputStream);
for(Sheet sheet:book){
for(Row row:sheet){
for(Cell cell:row){
System.out.println(cell.getStringCellValue());
//...
}
}
}
}
}
Note
解决了POI大文件内存容易溢出的问题
1.2 批量插入数据库(mybatis)
- 多次调用 void insert(Student)
START TRANSACTION;
insert into Student() values();
COMMIT;
START TRANSACTION;
insert into Student() values();
COMMIT;
...
Note
效率低,每次插入都会自动开启新事务,比较耗时
- 增加一个 void batchInsert(List)方法
START TRANSACTION;
insert into Student() values(),(),()...;
COMMIT;
Note
效率比上面高,但sql容易超长。(mybatis默认sql长度不能超过4m)
- 将JDBC改成批处理(ExecutorType.BATCH)
START TRANSACTION;
insert into Student() values();
insert into Student() values();
insert into Student() values();
...
COMMIT;
- 2+3结合使用
START TRANSACTION;
insert into Student() values(),(),()...;
insert into Student() values(),(),()...;
insert into Student() values(),(),()...;
...
COMMIT;
2. 异步/多线程 的多种写法
JDK1.8之前
Note
异步执行:直接新建一个Thread对象
public class Test{
public static void one(){
Thread thread = new Thread(){
@Override
public void run() {
try {
//停留1s,展示异步执行成功
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("线程ID:"+Thread.currentThread().getId()+" 输出:haha");
//
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
};
thread.start();
System.out.println("线程ID:"+Thread.currentThread().getId()+" 输出:heihei");
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
Note
异步执行:新建1个Runnable对象,放到线程池执行
public class Test{
public static void two(){
//定义一个任务
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//停留1s,展示异步执行成功
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("线程ID:"+Thread.currentThread().getId()+" 输出:haha");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
};
//定义一个线程池
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
threadPool.execute(runnable);
System.out.println("线程ID:"+Thread.currentThread().getId()+" 输出:heihei");
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
//记得关闭线程池
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}
Note
多线程执行:新建N个Runnable对象,放到线程池执行
public class Test{
public static void three() {
//需要定义:
// 1个计数器(CountDownLatch)
// 1个线程池(ExecutorService)
// 10个无返回值的任务(Runnable)
int TASK_NUM = 10;
//计数器
CountDownLatch cdl = new CountDownLatch(TASK_NUM);
//定义10个任务
List<Runnable> taskList = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<TASK_NUM;i++){
int finalNum = i;
taskList.add(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(finalNum * 1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("==========执行完毕!" + finalNum);
cdl.countDown();
});
}
//多线程执行任务
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
for(Runnable task:taskList){
threadPool.execute(task);
}
//等待所有任务执行完毕
System.out.println("==========wait!");
try {
cdl.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
//最后记得关闭线程池
threadPool.shutdown();
System.out.println("==========finish!");
}
}
Note
多线程执行&有返回值:新建N个FutureTask对象,放到线程池执行
public class Test{
public static void four() {
//需要定义:
// 1个计数器(CountDownLatch)
// 1个线程池(ExecutorService)
// 10个有返回值的任务(FutureTask + Callable)
int TASK_NUM = 10;
//计数器
CountDownLatch cdl = new CountDownLatch(TASK_NUM);
//定义10个任务
List<FutureTask<Integer>> taskList = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<TASK_NUM;i++){
int finalNum = i;
taskList.add(new FutureTask<>(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(finalNum * 1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("==========执行完毕!" + finalNum);
cdl.countDown();
return finalNum;
}));
}
//多线程执行任务
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
for(FutureTask task:taskList){
threadPool.execute(task);
}
//等待所有任务执行完毕
System.out.println("==========wait!");
try {
cdl.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
//取出计算结果并汇总。这里只是简单地求和。
int sum = 0;
for(FutureTask<Integer> task:taskList){
try {
sum+=task.get();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
System.out.println("==========result:"+sum);
//最后记得关闭线程池
threadPool.shutdown();
System.out.println("==========finish!");
}
}
Note
多线程执行&有返回值2:无需计数器
public class Test{
public static void five() {
//需要定义:
// 不用计数器(CountDownLatch)
// 1个线程池(CompletionService代替ExecutorService)
// 10个有返回值的任务(Callable)
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
CompletionService<Integer> cService = new ExecutorCompletionService<Integer>(threadPool);
int TASK_NUM = 10;
//定义10个任务
List<Callable<Integer>> taskList = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<TASK_NUM;i++){
int finalNum = i;
taskList.add(() -> {
return finalNum;
});
}
//执行任务
for(Callable task:taskList){
cService.submit(task);
}
//不用等到所有任务出结果才汇总
//先计算出结果的就可以先汇总
int sum = 0;
for(int i=0;i<TASK_NUM;i++){
try {
int result = cService.take().get();
System.out.println("==========执行完毕!" + result);
sum+= result;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
System.out.println("==========result:"+sum);
//最后记得关闭线程池
threadPool.shutdown();
System.out.println("==========finish!");
}
}
JDK1.8后
Note
异步执行,可使用CompletableFuture类来执行异步方法。写法简单
public class Test{
public static void one(){
//开启一个线程
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->{
System.out.println("线程ID:"+Thread.currentThread().getId()+" 输出:haha");
});
System.out.println("线程ID:"+Thread.currentThread().getId()+" 输出:heihei");
future.join();
}
}
Note
多线程执行&有返回值
public class Test{
public static void two() {
//需要定义:
// 不用计数器(CountDownLatch)
// 不用线程池(CompletableFuture自带线程池(ForkJoinPool.commonPool()))
// 10个有返回值的任务(Callable)
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
int TASK_NUM = 10;
//定义10个任务
AtomicInteger sum = new AtomicInteger();
List<CompletableFuture<Integer>> taskList = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<TASK_NUM;i++){
int finalNum = i;
//执行任务
taskList.add(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(finalNum * 1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("线程ID:"+Thread.currentThread().getId()+"==========执行完毕!结果:" + finalNum);
return finalNum;
}).thenApply(sum::addAndGet));
}
System.out.println("==========等待汇总结果!");
CompletableFuture
.allOf(taskList.toArray(new CompletableFuture[taskList.size()]))
.join();
System.out.println("==========result:"+sum);
//最后记得关闭线程池
threadPool.shutdown();
System.out.println("==========finish!");
}
}
3. 手工开启数据库事务
@Service
@Slf4j
public class TestServiceImpl implements TestService{
@Autowired
private TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate;
@Autowired
private StudentMapper studentMapper;
@Autowired
private TeacherMapper teacherMapper;
public void test(List<StudentDto> studentDtoList,List<TeacherDto> teacherDtoList){
transactionTemplate.execute(new TransactionCallbackWithoutResult() {
@Override
protected void doInTransactionWithoutResult(TransactionStatus transactionStatus) {
try{
studentMapper.batchInsert(studentDtoList);
teacherMapper.batchInsert(teacherDtoList);
}catch (Exception e){
log.error("保存报错",e);
transactionStatus.setRollbackOnly();
}
}
});
}
}
需要入参返回的可以这样写:
@Service
@Slf4j
public class TestServiceImpl implements TestService{
@Autowired
private TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate;
@Autowired
private StudentMapper studentMapper;
@Autowired
private TeacherMapper teacherMapper;
public void test(List<StudentDto> studentDtoList,List<TeacherDto> teacherDtoList){
Map<String,Object> result1 = transactionTemplate.execute(transactionStatus-> {
Map<String,Object> result = new HashMap<>();
try{
studentMapper.batchInsert(studentDtoList);
teacherMapper.batchInsert(teacherDtoList);
result.put("flag","Y");
}catch (Exception e){
log.error("保存报错",e);
transactionStatus.setRollbackOnly();
result.put("flag","N");
}
return result;
});
}
}
4. LocalDate的使用
| 日期时间类 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| LocalDate | 只包含年月日 |
| LocalTime | 只包含时分秒 |
| LocalDateTime | 包含年月日、时分秒 |
- 获取年月日、时分秒
LocalDate now = LocalDate.now(); //获取当前的年月日
System.out.println(now); //2024-05-28
System.out.println(now.getYear()); //2024
System.out.println(nowdata.getMonth().getValue());//4 获取当前月份
System.out.println(nowdata.getDayOfMonth());//6 获取今天几号
System.out.println(nowdata.getDayOfWeek().getValue());//2 获取今天星期几
System.out.println(nowdata.getDayOfYear());//96 获取今天是今年的第几天
Date nowDate = Date.from(now.atStartOfDay(ZoneId.systemDefault()).toInstant()); //LocalDate转成Date
System.out.println(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM").format(nextMonthFirstDay)); //按yyyy-MM转成字符串
//字符串按yyyy-MM格式转为LocalDate
LocalTime nowTime = LocalTime.now();
System.out.println(nowTime);//09:51:11.987 获取当前的时间
System.out.println(nowTime.getHour());//9 获取当前时间的小时
System.out.println(nowTime.getMinute());//51 获取当前时间的分钟
System.out.println(nowTime.getSecond());//11 获取当前时间的秒
5. Map <--> Object 转换示例
// Map 转 Bean
cn.hutool.core.bean.BeanUtil.mapToBean(map,StudentDto.class,false,null);
// Bean 转 Map
cn.hutool.core.bean.BeanUtil.beanToMap(studentDto);
// List<Map> 转 List<Bean>
List<Bean> beanList = mapList.stream().map(e->{
return BeanUtils.maptoBean(e,Bean.class);
}).collect(Collector.toList());
// Object 转 List<Bean>
6. Java8 Stream Collectors
6.1 集合转换
//1.1 list转成set(可以用来去重)
Set<String> personNameSet = personNameList.stream().collect(Collectors.toSet());
//1.2 list转成map(如果有重名,则取第一个)
Map<String,Person> personMap = personList.stream().collect(Collectors
.toMap(e->e.getPersonName(),e->e,(e1,e2)->e1));
6.2 分组
//按姓名分组
Map<String,List<Person>> personMap = personList.stream().collect(Collectors
.groupingBy(Person::getName);
//按班级+姓名分组
Map<String,List<Person>> personMap = personList.stream().collect(Collectors
.groupingBy(e->e.getClassName()+e.getName());
6.3 分组后操作
//按班级分组,并计数出每班总人数
Map<String,Long> classPersonCountMap = personList.stream().collect(Collectors
.groupingBy(Person::getClassName,Collectors.counting());
7. Java8 Stream Comparator
//对person List进行排序
//先根据名字升序排序
//再根据年龄降序排序
List<Person> sortedPersons = persons.stream()
.sorted(Comparator.comparing(Person::getName)
.thenComparing(Comparator.comparing(Person::getAge).reversed()))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
8. 时间是怎样定义的
GMT(格林威治标准时间)
1884年,国际经度会决定以经过格林尼治天文台(旧址) 的经线为本初子午线(0 度经线)。同时也将全球划分为了 24 个时区。0 度经线所在的时区为 0 时区。
UT(世界时)
UT在格林威治标准时间的基础上,增加了衡量一秒、一小时、一天究竟有多长的标准。
这个标准就是,UT会基于地球自转,来衡量时间的长度:
- 地球自转1圈定义为1天;
- 1小时为地球自转周期的1/24;
- 1秒则被定义为地球自转周期的1/86400。
UTC(世界协调时)
后来,人们意识到地球自转不是一个完全恒定的过程,地球会转得越来越慢。
地球的减速会导致每天的长度变长,每年大约增加1.7毫秒。
这样下去,会导致1秒的时间会越来越长。
为了追求1秒时间基本恒定,在不断寻找新的计时手段的努力下,人们发明了原子钟。
国际计量协会结合了全球 400 多个原子钟,规定 1 秒为铯-133 原子基态两个超精细能级间跃迁辐射震荡 9,192,631,770 周所持续的时间。 这个定义就叫国际原子时(International Atomic Time,TAI)。这样,我们钟表里指针应该转多快也有了一个统一的标准。
国际原子时的秒长以格林威治时间 1958 年 1 月 1 日 0 时的秒长为基准。也就是规定, 在这一瞬间,国际原子时的秒长和世界时的秒长是一样的。
闰秒
同时,引入闰秒的概念,来控制UT和UTC越来越大的误差。
所谓闰秒,也就是让在某个时间点上,人为规定这一分钟比普通的分钟多一秒,它有 61 秒。
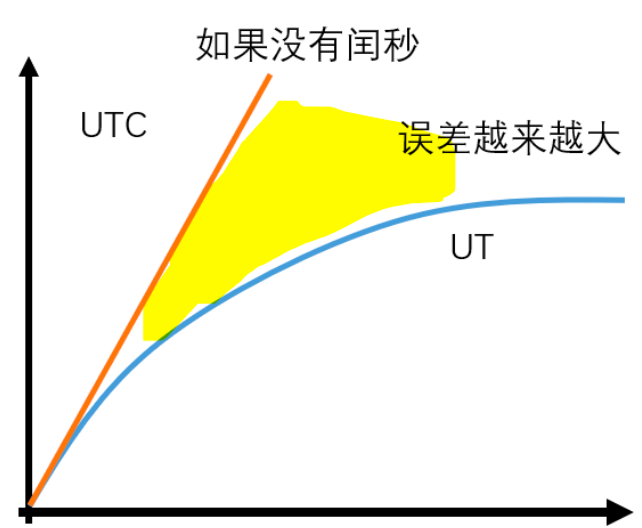
9. 时间的格式有哪些
ISO 8601
格式1:yyyy-MM-ddThh:mm:ssZ 示例1:2022-09-03T14:13:00Z ------- 用T隔开日期和时间,Z代表这是UTC或GMT时间,0时区。
格式2:yyyy-MM-ddThh:mm:ss.SSS+0000 示例2:2023-02-23T11:03:11.000+0000 --------用T隔开日期和时间,有3位代表微秒,加号后面4位表示时区
UNIX时间戳
Unix 时间戳只表示从特定时间点到现在的秒数。
GMT
格式:EEE,DD MMM YYYY HH:mm:ss GMT 示例1:Tue, 29 Nov 2022 03:30:28 GMT(0时区时间) 示例2:Tue, 29 Nov 2022 03:30:28 GMT+0800(中国标准时间)
CST
中国标准时间,跟GMT格式很相似。
注意,CST可以表示多个时区的时间:
- 美国中部时间(Central Standard Time)
- 澳大利亚中部时间(Central Standard Time)
- 中国标准时间(China Standard Time)
- 古巴标准时间(Cuba Standard Time)
因此使用CST格式的日期转成GMT可能会有错误。
格式:EEE MM DD HH:mm:ss CST YYYY 示例:Thu Aug 18 20:38:54 CST 2016
10. PageHelper
10.1 最常见的分页(先count再查询)
PageHelper.startPage(pageNum,pageSize);
List<YourEntity> result = findByExample(example);
return new PageInfo(result);
10.2 分页,但不执行count
Boolean isCount = false;
PageHelper.startPage(pageNum,pageSize,isCount);
List<YourEntity> result = findByExample(example);
return new PageInfo(result);
10.3 只count,不查询数据
// 使用PageHelper.startPage方法来设置分页参数,但不传入具体的pageSize和pageNum
PageHelper.startPage(1, 0);
List<YourEntity> result = findByExample(example);
// 使用PageInfo来获取总数
PageInfo<YourEntity> pageInfo = new PageInfo<>(result);
long total = pageInfo.getTotal(); // 这里获取的就是count的结果
11. 字符串操作
带参数的字符串---方法1:String.format()
// %s 字符串
// %d 整数
String formattedString = String.format("My name is %s and I am %d years old.", name, age);
带参数的字符串---方法2:MessageFormat.format()
String greeting = MessageFormat.format("你好,{0},你今年{1}岁,是一名{2}。", name, age, job);
下划线转驼峰:cn.hutool.core.util.StrUtil.toCamelCase()
String camelStr = StrUtil.toCamelCase(underLineStr);
EasyExcel拦截器的运用
- AbstractWorkbookWriteHandler
- AbstractRowWriteHandler
- AbstractCellWriteHandler(已废弃)
- CellWriteHandler接口
- HorizontalCellStyleStrategy
- AbstractVerticalCellStyleStrategy
ExecutorService
ExecutorService是一个线程池接口,有2种方式可以初始化:
//方法1:直接new一个对象(推荐)
ExecutorService executorService = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
5, //核心线程数
50, //最大线程数
0L, //空闲线程存活时间
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, //存活时间单位
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(), //工作队列
new ThreadFactoryBuilder().setNameFormat("batch-update-total-account-thread-%d").build(), //线程工厂:自定义线程命名格式
new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy() //拒绝策略
);
【工作队列】
当已经没有空闲线程可以执行新任务时,便会将新任务放到工作队列,等待执行。
可选的工作队列:
| JAVA类 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| SynchronousQueue | 不存储任务,当线程池达到最大线程数时,新任务会立即触发拒绝策略 |
| LinkedBlockingQueue | 可以无限堆积任务,不会触发拒绝策略。但有可能导致OOM |
| ArrayBlockingQueue | 可以控制队列大小,防止资源耗尽 |
| PriorityBlockingQueue | 可以按优先级处理任务 |
拒绝策略
当线程池无法接受新任务时,便会执行拒绝策略。如:
- 线程池已关闭
- 线程池工作队列已满(对于有界队列)
- 线程池已达到最大线程数且无法创建新线程
可选拒绝策略:
| JAVA类 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy | 默认策略,直接抛出RejectedExecutionException异常 |
| ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy | 由提交任务的线程(即主线程)自己执行该任务 |
| ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy | 静默丢弃无法处理的任务,不做任何通知 |
| ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy | 丢弃队列中最老的一个任务,然后尝试重新提交当前任务 |
//方法2:使用Executors工具类
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
通过下面的方法,往线程池添加一个任务。
ExecutorService.submit(()->{});
添加完后,任务会自动在后台运行,主线程不会被阻塞。
12. @Transactional注解失效的场景
- 方法不是public的:@Transactional注解只对public方法有效,如果方法是private、protected或default的,则不会被事务管理。
- 方法被调用时没有通过代理:如果方法被直接调用,而不是通过代理(如Spring AOP),则@Transactional注解不会生效。
- 方法抛出的异常不是RuntimeException:如果方法抛出的异常不是RuntimeException或其子类,则事务不会回滚。
- 方法中有try-catch块:如果方法中有try-catch块,并且catch块中没有重新抛出异常,则事务不会回滚。
- 方法被调用时事务已经存在:如果方法被调用时已经存在一个事务,则新的@Transactional注解不会生效。
- @Transactional注解被重复定义:如果同一个类中有多个方法都被标注了@Transactional注解,则只有第一个方法的注解会生效。
- @Transactional注解被定义在抽象类或接口中:如果@Transactional注解被定义在抽象类或接口中,则不会生效。
- 方法被调用时使用了线程池:如果方法被调用时使用了线程池,则@Transactional注解可能不会生效,因为事务上下文(如TransactionSynchronizationManager)是线程绑定的,只要是在异步线程执行,则不会继承原线程的事务。
- 方法被调用时使用了异步调用:如果方法被调用时使用了异步调用(如Spring的@Async注解),则会开启新线程,@Transactional注解不会生效。
13. 如何保证同表不同库的数据一致性(mysql、es、mongodb)
使用中间件Canal
14. 常见的SpringBoot配置
# 数据库事务超时配置